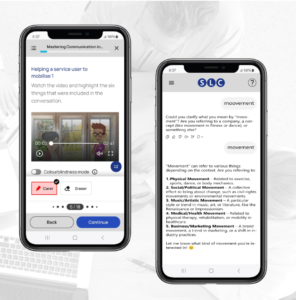
SLC win Ufi grant to develop AI language learning app for social carers
We’re delighted to have won a grant from Ufi VocTech Trust to develop an AI-driven technology solution that provides cheap phone-based language and communication skills
This lesson enables students to describe different types of medication, how they are administrated and how they work. It is relevant for nursing and care students and professionals.
B1 (lower-intermediate) level
Note: this article introduces the first part of the Teachers Notes. There is a link at the bottom to download the complete set of Teachers Notes and the Student Worksheet, so you can use this in your lessons.
● Topic: Types of medications
● Timing: 30–50 minutes
● Lesson type/focus: speaking, reading, vocabulary and writing
● Speaking: discuss types of medications
● Reading: read for specific information
● Vocabulary: learn and review language for types of medications
● Writing: practise organising and presenting information
The focus of the lesson is describing types of medication. The speaking activity introduces the topic and gives students the opportunity to share their ideas and experience. The reading activity introduces some more related language and practises reading for specific information. The vocabulary activities introduce/review key vocabulary. The writing activity uses language from the lesson and students’ own knowledge to produce a piece of patient-centred writing.
Note: This lesson supports the language introduced in the following:
● Course: English for Nurses: Getting the Essentials Right
● Unit: Administrating Medications
● Module: ‘Types of medication’ pages 7, 11 and 14
Put students into pairs or small groups and ask them to discuss questions 1–3 on the student worksheet. Encourage them to share examples from their own experience.
Do whole class feedback to discuss and share answers.
Have students work individually to read the text and reorder the sentences to complete the definitions. Then have them compare their ideas with a partner.
Go through the answers as a class.
Have students read the text through again individually and highlight any new words. Deal with any vocabulary queries.
1. Absorption: medication enters the bloodstream and becomes bioavailable
2. Distribution: medicine passes out of the bloodstream across the cell membrane
3. Metabolism: unwanted medicine becomes water-soluble
4. Excretion: unused medical waste passes out of the body through body fluids
Extension activity
Have students work individually, or in pairs, to write five questions for the text. Then have them swap their questions and answers them. Alternatively, set five comprehension questions yourself.
Example questions:
Which kind of medicines are absorbed the fastest? intravenous medicines
Why does the absorption rate of oral medication vary? amount of stomach acid, food or other medications in stomach
How does medication get out of the bloodstream? by passing across the cell membrane
What does the blood-brain barrier do? stops medication entering the brain
What happens to parts of the medication the body doesn’t need? it is excreted by the kidney
Download the complete lesson plan and student worksheet:

We have many more available on our partner’s website. EALTHY is a unique international association for
English for Healthcare teachers, writers and researchers. It offers members a growing bank of lesson plans, OET resources, articles and research summaries, as well as free and discounted access to conferences, journals, publications and SLC courses!
Through our partnership, we publish at least three new plans in the EALTHY Members Area every week. So, if you’re a teacher looking for excellent resources, now is the time to join an international English for Healthcare community and take advantage of everything EALTHY has to offer.
Annual memberships are available for teachers and for institutions. We hope very much to see you there!
Get your monthly updates and latest materials on Medical English

We’re delighted to have won a grant from Ufi VocTech Trust to develop an AI-driven technology solution that provides cheap phone-based language and communication skills

We’re delighted to announce a partnership with leading Medical English app, Doxa.
