
A Year to Celebrate: Thank You for Being Part of Our 2025 Journey
As 2025 comes to a close, we’ve been reflecting on what has truly been an inspiring and rewarding year for Specialist Language Courses. It has
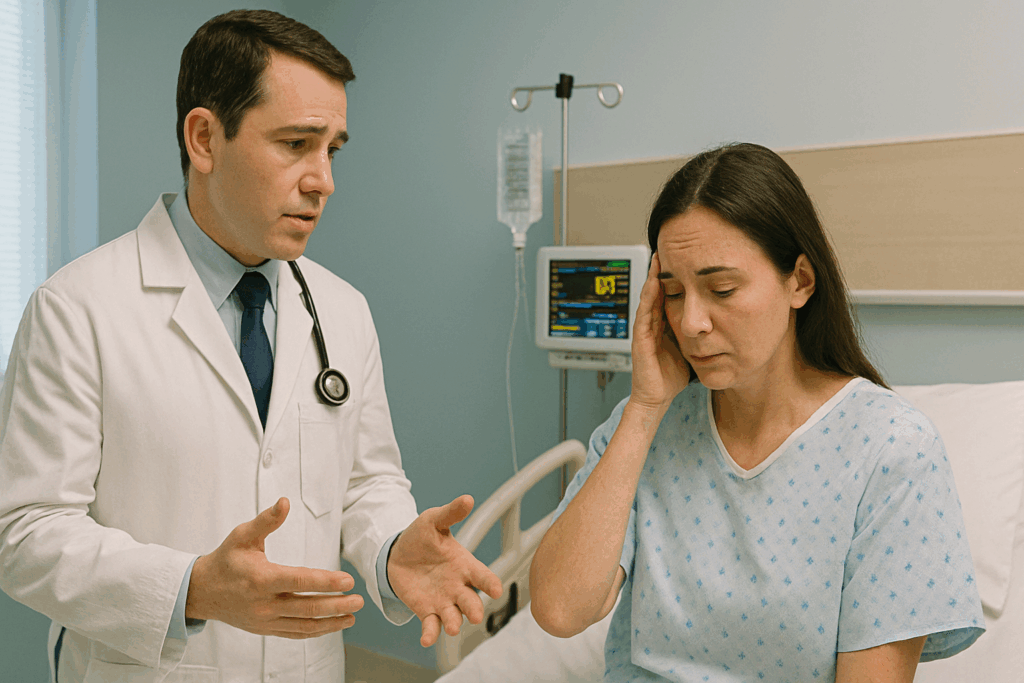
Breaking bad news is one of the most challenging tasks for healthcare professionals. It requires a careful balance of empathy, clarity, and professionalism. For learners of Medical English, mastering this type of communication is especially important—not just for exams like OET but also for their daily clinical practice.
As teachers, we can help students build the language, confidence, and sensitivity needed to handle these conversations effectively.
Use the following frameworks with your students to help them structure these types of conversations.
A widely used six-step framework for delivering bad news:
Recently developed to support interpreters and healthcare professionals:
Manage the conversation
Include the following in your tutored sessions.
Teaching the language of breaking bad news in Medical English goes far beyond vocabulary—it’s about developing empathy, clarity, and cultural sensitivity. By introducing learners to frameworks like SPIKES, practising role-plays, and focusing on emotional awareness, teachers can give healthcare professionals the tools to navigate these conversations with confidence.
Ultimately, strong communication skills in difficult moments improve patient care, build trust, and ensure that medical English learners succeed both in their exams and in their clinical practice.
The most common mnemonic is SPIKES, a six-step protocol used to guide healthcare professionals when delivering difficult information. It stands for:
This structure helps ensure clarity, empathy, and professionalism.
Healthcare professionals often use empathetic phrases such as:
Expressions should balance clarity, sensitivity, and reassurance, avoiding overly technical or harsh language.
Breaking bad news in medicine involves:
Frameworks such as SPIKES or CALM are often taught in medical communication training.
SBAR is a communication tool used in healthcare to structure information between professionals. It stands for:
While not specific to breaking bad news, SBAR helps ensure clear and concise handovers, especially in urgent or high-pressure situations.

As 2025 comes to a close, we’ve been reflecting on what has truly been an inspiring and rewarding year for Specialist Language Courses. It has

We are proud to announce the development of a new OET preparation course for all Professions, designed for healthcare professionals preparing for OET in: Dentistry,

We’re delighted to have been commissioned to provide an online ESOL programme for refugee and migrant learners by the South East Strategic Partnership for Migration
Get updates and get the latest materials on Medical English, OET and IELTS
